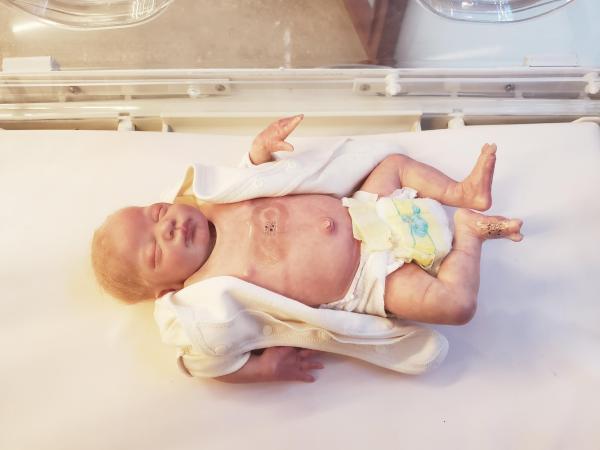
Smoking during pregnancy increases the risk that your baby will become obese
IMAGE: This is Kevin Pearson in his lab at the University of Kentucky. view more Credit: UK Photo | Mark Cornelison LEXINGTON, Ky. (Jan. 4, 2019) — Using foreskin tissue from newborn circumcisions, a group of researchers have identified a potential cellular mechanism that connects a mother’s smoking while pregnant with an increased risk of offspring…
Details