Greek Wines Get Back to Their Roots
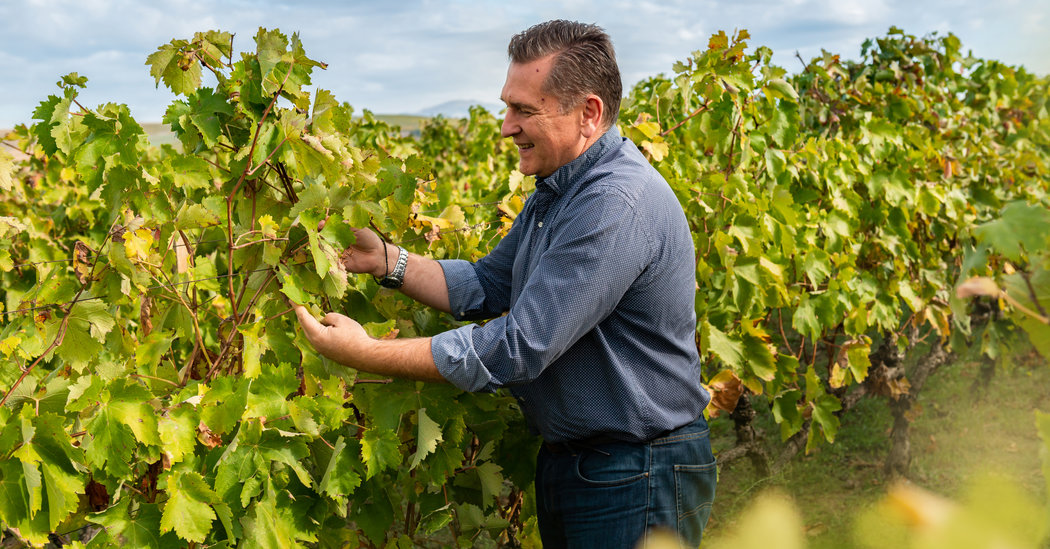
AMYNDEON, Greece — The landscape of the Macedonian region in northern Greece is tapestried with vineyards. They supply wineries that are producing some of the best red wines Greece has to offer. The Alpha Estate here in the northwestern corner of Macedonia is a fine example. In a tasting of Greek reds by the wine…
Details