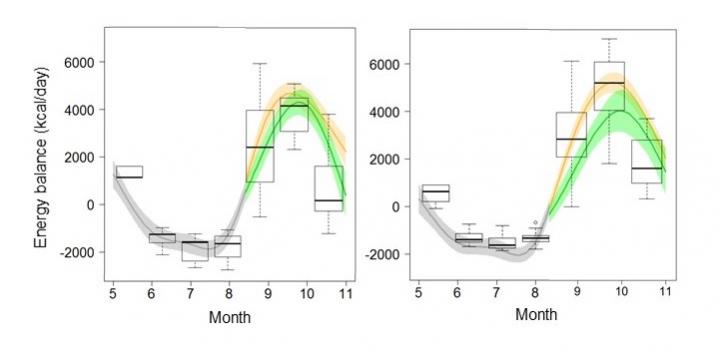
A collaboration led by scientists at Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT), Japan, has discovered that daily energy balance of Asian black bears (Ursus thibetanus) exhibited seasonal change with a twin-peak pattern: up in spring, down to the lowest point in summer, and up again in autumn. From spring to summer, the energy balance is surprisingly negative. Interestingly, bears obtain about 80% of the energy they need in a year by eating acorns in autumn.
Energy balance (i.e., energy intake minus energy usage) is an essential factor when evaluating an animal’s nutritional state. “We aimed to identify periods of the year that are most important for Asian black bears in terms of energy balance,” said the senior and corresponding author Dr Shinsuke Koike, associate professor at TUAT. “We estimated daily energy balance of 34 bears fitted with GPS collars in the central Japan as follows. Energy intake of bears was estimated using the energy content (kcal/g) of major food items, their average ingestion rate (g/min), and daily feeding time (min). Then, energy usage was calculated by an equation for the costs of resting, traveling, and feeding based on behavioral data monitored by the GPS collars.”
Because food habits of bears change seasonally, each month scientists estimated the daily energy balance. Also, because bears change their feeding behavior depending on the availability of hard mast, they made separate estimations for years of good and poor mast conditions during autumn. The scientists then identified major food items from fecal analysis and calculated the gross energy content per unit for each item.
“We have been directly watching bears feeding over 10 years. And we measured ingestion rates of the major food items; acorns on the tree had the highest ingestion rate, while the values of other items did not show notable characteristics,” said Koike. “We obsterved that the variability of energy expenditure rose moderately in good mast years, except for males. On the other hand, there was a twin-peak pattern of energy intake and energy balance, declining from May to July, rising again from August to October, and declining in November.”
“Interstingly, only for females, the peak of energy intake and energy balance was larger in good mast years than in poor mast years, while the cumulative energy balance in good mast years was larger than in poor mast years for both females and males. After poor mast years, the cumulative energy balance of males become negative in February, during hibernation, and did not exceed zero until August, even if they could start feeding in May,” Koike explains. “Thus, further longitudinal studies that examine cumulative energy balance, rather than energy balance alone, are necessary to clarify the seasonal change in the nutritional state of Asian black bears” adds Koike.
###
For information about the Koike laboratory, please visit //web.
This research was supported by Grants- in-Aid for Scientific Research (Nos. 16H04932, 17H05971, 17H00797, 16H04939, and 19H02990) and the Pollution Control Research Fund from the Ministry of the Environment, Japan, funded this work.
About Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT):
TUAT is a distinguished university in Japan dedicated to science and technology. TUAT focuses on agriculture and engineering that form the foundation of industry, and promotes education and research fields that incorporate them. Boasting a history of over 140 years since our founding in 1874, TUAT continues to boldly take on new challenges and steadily promote fields. With high ethics, TUAT fulfills social responsibility in the capacity of transmitting science and technology information towards the construction of a sustainable society where both human beings and nature can thrive in a symbiotic relationship. For more information, please visit //www.
Original publication:
Furusaka S, Tochigi K, Yamazaki K, Naganuma T, Inagaki A, Koike S.
Estimating the seasonal energy balance in Asian black bears and associated factors
Ecosphere, 10, e02891 (2019)
https:/
Contact:
Shinsuke Koike, Associate professor, Laboratory of Forest Conservation Biology, Graduate School of Agriculture, TUAT, Japan
koikes@cc.tuat.ac.jp
Disclaimer: AAAS and EurekAlert! are not responsible for the accuracy of news releases posted to EurekAlert! by contributing institutions or for the use of any information through the EurekAlert system.

