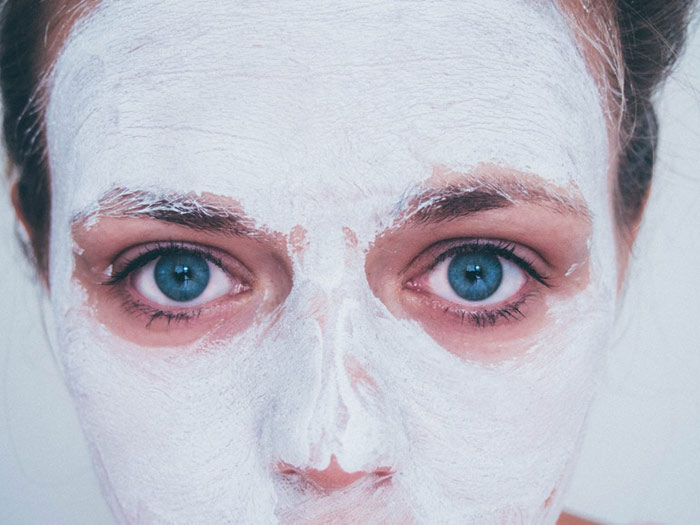
Cells on human skin die every 30 days. Their particles clog the pores and block the access of oxygen to other skin cells. A peeling procedure removes the dead cornified layer from the skin surface, transforms and refreshes the face. The market of peeling procedures is so diverse today that you can undergo them in the salon and at home. The most common care procedures, however, have a number of contraindications. Who should abandon peeling?
Why is frequent peeling a No-Go?
Peeling cannot be carried out frequently because the skin becomes thinner after exposure to chemical compounds; the cell life cycle is shortened, and acidic compounds can provoke gradual scarring of the tissue and the formation of rosacea. Below we will provide a list of the most common symptoms and diseases when peeling procedures are contraindicated.
Dry irritated skin
Patients with dry, irritated, exfoliating skin, which is prone to itching, cracks, and damage, should not visit peeling procedures. They may have symptoms of xerosis or abnormal drying of the skin, which can be a sign of skin diseases or a reaction to external factors: wind, frost, or poor ecology. This person’s face looks inflamed and red, with visible lesions, and the pores are almost invisible.
Such skin requires very careful and gentle care, and peeling can enhance the destruction of the dermis cells. Fissures on the face let potentially dangerous chemicals and acids used during the procedure penetrate into the tissues and cause deep chemical burns and irreversible damage.
Acne
Inflammations on the face are also an absolute contraindication to peeling. Acne, pyoderma, pustular rash, caused by staphylococci and streptococci, under certain conditions can provoke the development of acute inflammation. Active reproduction of bacteria leads to the response of the dermis and provokes edema and lymphostasis. A peeling or exfoliation procedure, which includes exfoliation of the upper skin layers with microdamage, can seriously aggravate the problem, increase puffiness, impair lymphatic circulation, and remove the protective barriers, thus enabling penetration of the infection into the deeper layers of the skin.
In addition, such microtraumas are a provoking factor for the herpes infection. Strong peeling can cause primary infection. The risk group includes patients with recurrent herpes, with reduced immunity, prone to skin inflammation, as well as chronic dermatological pathologies: eczema, psoriasis, dermatitis, etc.
Couperose
Vascular mesh or vascular stars on the face are the first manifestation of couperose, a disease in which the capillaries become dilated, fragile and brittle due to the sensitivity of the skin and impaired blood microcirculation. Couperose is a genetic disease that a person can exacerbate, for example, by excessive drinking alcohol, which produces a vasodilating effect; or eating hot and spicy foods and drinks; sudden changes in temperature; ultraviolet radiation on the skin, as well as stress and nervous overstrain.
The effects of chemical or acid peeling on the skin with signs of couperose will lead to increased blood flow in the affected area, stagnation in the blood vessels of the skin and their additional excessive fragility and damage.
Hyperpigmentation
Speaking about hyperpigmentation, we mean foci and areas on the face or neck that are excessively stained with dark pigment. We are not always aware of the nature of such phenomena. As you know, pigmentation can be congenital (manifested as freckles or birthmarks) and acquired. In this case, we are talking about skin diseases, such as chloasma and melasma, which are often associated with hormonal disorders, urinary and digestive system pathologies, kidney disorders or violation of metabolic processes.
Traumas, cancer, inflammation in the skin, excessive sun exposure, and antibiotics are frequent causes of hyperpigmentation.
Due to the high concentration of acids, medium and deep peeling affect the dermis so deeply that they can provoke the destruction of the epidermal layer, an inflammatory process in them, as well as vascular complications.
Allergy
The composition of peeling medications include substances such as pyruvate, lactate, carboxylic acids, retinol, salicylic acid, which are toxic and can cause intolerance in patients prone to various types of allergies. Such an aggressive immune response of the body can lead to serious complications.
When a chemical substance comes in contact with the skin, histamine is released, which can cause swelling. Peeling allergy is a frequent adverse reaction in cosmetology. Most often, it is caused by intolerance of the chemical substance rather than by mechanical procedures. Depending on how deeply the drug penetrates the dermis, the symptoms of complications will appear. The reaction after peeling occurs immediately after the procedure. There is a slight redness, the burning sensation increases with every minute; there are intense itching and swelling of the skin.
To avoid such consequences and to ensure safety, cosmetologists usually perform a skin test in the area of the elbow crease or wrist before starting the procedure.